Building a command-line tool with libtopotoolbox#
libtopotoolbox provides a set of functions for analyzing digital elevation models. These functions operate on data passed in to them, and they do not take care of memory management or reading data from files. The bindings for libtopotoolbox in other languages such as Python and MATLAB allow you to use the facilities of those languages and their geospatial ecosystems to manage your data and pass it to libtopotoolbox in the required format.
In this tutorial, we will build a small command line application in C
that fills sinks in digital elevation models. We will use
libtopotoolbox’s fillsinks function and GDAL for data input and output.
Setting up the project#
The simplest way to build a C or C++ project using libtopotoolbox is CMake. We’ll start by creating a new CMake project for our command line application. If you would like more information on using CMake, check out their documentation, especially the CMake Tutorial.
Create a new directory for the application. and then create the file
CMakeLists.txt in that directory in a text editor.
Start that file by declaring a new project:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.14)
project(
fillsinks
VERSION 0.0.1
LANGUAGES C
)
These lines define the minimum CMake version that we will support and
create a new project with the name fillsinks.
We tell CMake to build an executable program called fillsinks by
adding the following at the end of our CMakeLists.txt:
add_executable(fillsinks fillsinks.c)
We tell CMake that the source code for our fillsinks program will be
in a file called fillsinks.c. Create fillsinks.c in the same
directory as CMakeLists.txt and add a minimal main function.
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
return 0;
}
At this point, you should be able to build and run the program. From the terminal in your source directory, run
> cmake -B build
> cmake --build build
> build/fillsinks
cmake -B build creates the CMake buildsystem for your operating
system and C compiler and stores everything it needs in the build/
directory. The second line, cmake --build build runs the build
step. You should see some output that shows the fillsinks target
being built. The last line runs our program. Our program immediately
returns 0, so you shouldn’t see anything at this point.
Before we start building our application, let’s make sure that CMake
can find GDAL and libtopotoolbox. After the project lines but before
the add_executable in CMakeLists.txt, add
include(FindGDAL)
include(FetchContent)
FetchContent_Declare(
topotoolbox
GIT_REPOSITORY https://github.com/TopoToolbox/libtopotoolbox.git
GIT_TAG main
)
FetchContent_MakeAvailable(topotoolbox)
include(FindGDAL) uses the FindGDAL CMake module to find the GDAL
library installed on your system. The following lines use FetchContent
to download the latest version of libtopotoolbox from its GitHub
repository. Finally, we need to tell CMake to link GDAL and
libtopotoolbox to our executable. Finally, after the add_executable
line, add
target_link_libraries(fillsinks GDAL::GDAL topotoolbox)
Now run the CMake build again
> cmake -B build
> cmake --build build
The first command should output something like Found GDAL to
indicate that it succesfully found GDAL on your system, and the second
should show that CMake builds the libtopotoolbox library alongside our
executable.
Reading data with GDAL#
Our command line program will read elevation data from a file using GDAL. This section closely follows GDAL’s Raster API Tutorial.
Begin by including the GDAL header files and some necessary C
standard library headers at the top of fillsinks.c.
#include <gdal.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stddef.h>
Open a GDAL dataset from the filename passed on the command line
by adding the following code to the beginning of the main
function.
if (argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: fillsinks <filename>\n");
return -1;
}
char *filename = argv[1];
GDALAllRegister();
GDALDatasetH hDataset = GDALOpen(filename, GA_ReadOnly);
if (hDataset == NULL) {
printf("Unable to open %s\n",filename);
return -1;
}
GDALDriverH hDriver = GDALGetDatasetDriver(hDataset);
Now, continuing in main, allocate an array to hold the DEM and read
the data from the file into that array.
ptrdiff_t xsize = GDALGetRasterXSize(hDataset);
ptrdiff_t ysize = GDALGetRasterYSize(hDataset);
float *dem = malloc(sizeof(*dem) * xsize * ysize);
if (dem == NULL) {
printf("Unable to allocate memory for DEM\n");
GDALClose(hDataset);
return -1;
}
GDALRasterBandH hBand = GDALGetRasterBand(hDataset,1);
if (GDALRasterIO(hBand, GF_Read, 0, 0, xsize, ysize, dem, xsize, ysize,
GDT_Float32, 0, 0) != CE_None) {
printf("Error reading from dataset\n");
free(dem);
GDALClose(hDataset);
return -1;
}
We have hardcoded band number 1 in GDALGetRasterBand. The allocated DEM
is an array of single-precision floating point numbers, which is
required by libtopotoolbox’s fillsinks function. GDALRasterIO
automatically converts the data in the file to the correct data type
(GDT_Float32).
Filling sinks with libtopotoolbox#
To use libtopotoolbox in our code, we need to include the header file
at the top of fillsinks.c.
#include <topotoolbox.h>
According to the header file and the libtopotoolbox API documentation,
fillsinks has the following signature.
void fillsinks(float *output, float *dem, ptrdiff_t dims[2]);
dem is a pointer to the input data, an array of size dims[0] *
dims[1]. dims[0] refers to the dimension that changes the
fastest as you step through the array in memory while dims[1]
refers to the slowest changing dimension. For data read by GDAL, this
means that dims[0] corresponds to the X dimension (xsize) and
dims[1] corresponds to the Y dimension (ysize).
The output array must be the same size as the input array, and we
must allocate it ourselves following our GDAL reading code in main.
float *output = malloc(sizeof(*output)*xsize*ysize);
Following that, we have what we need to call fillsinks:
ptrdiff_t dims[2] = {xsize, ysize};
fillsinks(output, dem, dims);
The output array now contains the DEM with all of the sinks removed
using a grayscale morphological reconstruction algorithm.
Writing data with GDAL#
To write our the output data to a file, we’ll use GDALCreateCopy to
create a new dataset with the same georeferencing information as the
input DEM and then write the output array.
GDALDatasetH outDataset = GDALCreateCopy(hDriver, "filled_dem.tif", hDataset,
FALSE, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (outDataset == NULL) {
printf("Unable to create output dataset\n");
free(output);
free(dem);
GDALClose(hDataset);
}
GDALRasterBandH outBand = GDALGetRasterBand(outDataset, 1);
if (GDALRasterIO(outBand, GF_Write, 0, 0, xsize, ysize, output, xsize, ysize,
GDT_Float32, 0, 0 ) != CE_None) {
printf("Unable to write output data\n");
};
And finally we will free all of our resources including the GDAL
datasets. Closing the output dataset is necessary to ensure that the
data are properly written to the disk. Finish the main function with
the following, just before the return statement.
GDALClose(outDataset);
GDALClose(hDataset);
free(output);
free(dem);
The complete code for both CMakeLists.txt and fillsinks.c can be
found below (Complete code).
Compiling and running#
Since we haven’t changed the build configuration, we don’t need to run
the first configuration step (cmake -B build), but only the second,
compilation step
> cmake --build build
We can now run our program on some data. Example DEMs can be found in the TopoToolbox/DEMs repository.
> build/fillsinks tibet.tif
There should now be a file called filled_dem.tif in your current
directory containing the sink-filled DEM.
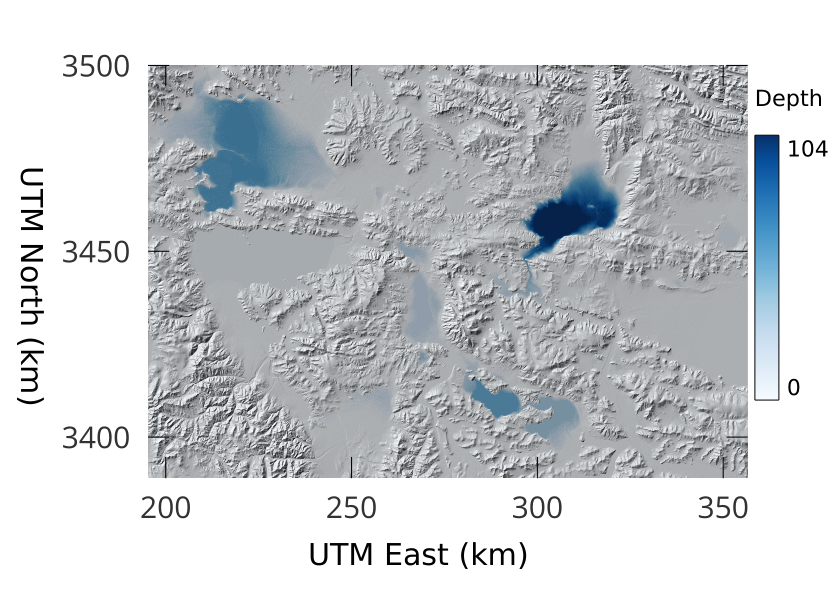
The difference between the filled Tibet DEM and the original, displayed over a hillshade of the original DEM.#
Summary#
To incorporate libtopotoolbox into a project you should:
Set up your compiler or build system so that it can find libtopotoolbox. CMake can help do this automatically.
Include the header file
topotoolbox.h, which can be found in theinclude/directory of libtopotoolbox, in your C program.Load DEM data into your program using whichever methods you prefer. libtopotoolbox does not perform any input or output on its own.
Allocate memory for all the necessary input, output and temporary data structures that the function requires. See the API documentation for details. libtopotoolbox does not allocate any memory.
Call the desired libtopotoolbox functions.
This procedure is roughly the same whether you are creating a simple command line application like we did here, integrating libtopotoolbox into a larger system like a GIS or creating new bindings for other programming languages.
Complete code#
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.14)
project(
fillsinks
VERSION 0.0.1
LANGUAGES C
)
include(FindGDAL)
include(FetchContent)
FetchContent_Declare(
topotoolbox
GIT_REPOSITORY https://github.com/TopoToolbox/libtopotoolbox.git
GIT_TAG main
)
FetchContent_MakeAvailable(topotoolbox)
add_executable(fillsinks fillsinks.c)
target_link_libraries(fillsinks GDAL::GDAL topotoolbox)
fillsinks.c
#include <gdal.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <topotoolbox.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: fillsinks <filename>\n");
return -1;
}
char *filename = argv[1];
GDALAllRegister();
GDALDatasetH hDataset = GDALOpen(filename, GA_ReadOnly);
if (hDataset == NULL) {
printf("Unable to open %s\n",filename);
return -1;
}
GDALDriverH hDriver = GDALGetDatasetDriver(hDataset);
ptrdiff_t xsize = GDALGetRasterXSize(hDataset);
ptrdiff_t ysize = GDALGetRasterYSize(hDataset);
float *dem = malloc(sizeof(*dem) * xsize * ysize);
if (dem == NULL) {
printf("Unable to allocate memory for DEM\n");
GDALClose(hDataset);
return -1;
}
GDALRasterBandH hBand = GDALGetRasterBand(hDataset,1);
if (GDALRasterIO(hBand, GF_Read, 0, 0, xsize, ysize, dem, xsize, ysize,
GDT_Float32, 0, 0) != CE_None) {
printf("Error reading from dataset\n");
free(dem);
GDALClose(hDataset);
return -1;
}
float *output = malloc(sizeof(*output)*xsize*ysize);
ptrdiff_t dims[2] = {xsize, ysize};
fillsinks(output, dem, dims);
GDALDatasetH outDataset = GDALCreateCopy(hDriver, "filled_dem.tif", hDataset,
FALSE, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (outDataset == NULL) {
printf("Unable to create output dataset\n");
free(output);
free(dem);
GDALClose(hDataset);
}
GDALRasterBandH outBand = GDALGetRasterBand(outDataset, 1);
if (GDALRasterIO(outBand, GF_Write, 0, 0, xsize, ysize, output, xsize, ysize,
GDT_Float32, 0, 0 ) != CE_None) {
printf("Unable to write output data\n");
};
GDALClose(outDataset);
GDALClose(hDataset);
free(output);
free(dem);
return 0;
}
